Linkage and Crossing Over
Linkage and Crossing Over: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Linkage, Crossing Over, Linkage Maps, Linkage Groups and, Mechanism of Linkage
Important Questions on Linkage and Crossing Over
Morgan observed tight linkage in Drosophila with only 1.3 percent recombination for:
Frequency of recombination between gene pairs on same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes to map their position on chromosome, was used for the first time by
If yellow body, white eyed drosophila is crossed with wild brown body red eyes drosophila. Then what would be the frequency of recombinants in generation?
Find out the incorrect statement.
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | T. H. Morgan | (i) | Chromosome theory |
| (b) | Hugo de Vries | (ii) | Gene mapping |
| (c) | Sutton and Boveri | (iii) | Linkage |
| (d) | Alfred Sturtevant | (iv) | Mutation |
| (v) | Hybrid experiments |
Imagine that in the pea plants the factors for controlling seed coat colour and shape of seeds are present on the same chromosome very close together. Performing dihybrid experiments with these characters, Mendel would not have been able to arrive at the idea to
What happens when two genes are situated very close to each other in a chromosome?
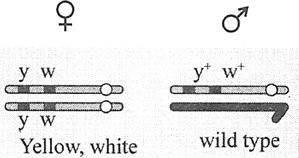
The cross given below was conducted by Morgan on Drosophila.
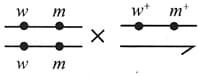
In generation, progeny had parental and recombinant traits in the ratio of . Determine the percentage of progeny which would lead to the given condition?
In a test cross of plant, the following progeny is obtained:
What is the distance between genes and
Linkage and crossing over are
Read the following statements and state true (T) or False (F):
A. T. H. Morgan worked with tiny fruit flies Drosophila melanogaster.
B. Morgan studied genes that were sex linked.
C. Morgan observed that two genes did not segregate independently of each other and undefined ratio was deviated from undefined
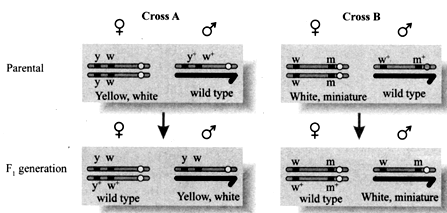
The experiment shown in the figure below has been carried out by Morgan to show the phenomenon of linkage and recombination. If in cross I, genes are tightly linked and in cross II, genes are loosely linked, then what will be the percentage of recombinants product in cross I and cross II, respectively?
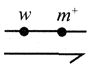
Which of the following gene combination is suitable for experiments on linkage?
Distance between the percentage of recombination and the genes shows
Which of the following will not lead to variations among siblings?
The variation in cross overs will be ______ depending upon the distance between any two genes which is inversely proportional to the strength of linkage.
Match List-I with List-II
| List-I | List-II | ||
| (A) | Morgan | (I) | Induced mutations |
| (B) | Lysenko | (II) | Photoperiodism |
| (C) | Muller | (III) | Term 'Genetics' |
| (D) | Garner and Allard | (IV) | Vernalization |
| (V) | Linkage |
According to the cross given below in Drosophila, if selfing of generation is made, the result observed by Morgan was
If map distance between genes P and Q is units, between P and R is units, and between Q and R is units, the order of genes on the linkage map can be traced as follows:
